Lecture Exercises
Table 1: How Do You Make ATP from Glucose?
| Location | Starts with | Ends with | Stored Forms of Energy (ATP, NADH, or FADH2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycolysis | Cytoplasm | glucose (C 6H 12O6) + 2 ATP + 2 NAD+ | 2 pyruvate (C 3H 4O3) + 2 (net) ATP + 2 NADH | ATP |
| Pyruvate oxidation | mitochondrial matrix | 2 pyruvate + 2 NAD+ + 2 Coenzyme A complexes | 2 acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) + 2 CO2 + 2 NADH | NADH |
| Citric Acid Cycle | mitochondrial matrix | 2 acetyl CoA + 6 NAD+ + 2 FAD (+ oxaloacetate ) | oxaloacetate + 4 CO2 + 2 ATP + 6NADH + 2 FADH2 | FADH2 |
| Oxidative Phosphorylation |
Lecture Notes
In cellular respiration the energy is transferred to the bonds between the phosphate groups ATP.
ATP can be used by cells as a source of energy by breaking the high-energy phosphate bonds.
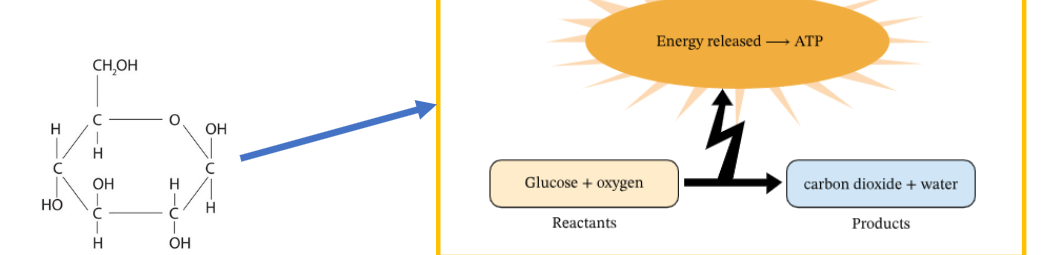 The energy in glucose is stored in the chemical bonds between the atoms. It is not directly available for your cells to use.
The energy in glucose is stored in the chemical bonds between the atoms. It is not directly available for your cells to use.