Software evolution
Software change
- Software change is inevitable
- new requirements emerge when software is used
- the business enviornments change
- errors must be repaired
- new computers and equipment is added to the system
- the preformance or reliability of system may have to be improved
- A key problem for organizations is implementing and managing changes to their existing Software Systems
Program evolution dynamics
- PED is the study of processe of system change
Lehmans law
- continuing change
- A program that is used in the real world must change progressivly to be useful
- Increasing complexity
- As program evolves and changes its infrastructure becomes more complex
- Large program evolution
- Program evolution is a self-regulating process.
- Organizational stability
- Over a programs lifetime the rate of development is constant and independent of the resources devoted to it
- Conservation of familiarity
- The incremental change in each release is constant
- Continuing growth
- The functionality has to continue to grow to maintain users
- Declining quality
- The quality of the system will appear to be declining unless tehy are adapted to changes in their operational env.
- Feedback System
Applicability of Lehmans Law
Lehmans law seems to be generally applicable to large tailored systems dev. by large organizations
its not clear on how to modify
- shrink-wraped software products
- systemtshat incorporate a lot of COTS componenets
- Small organizations
- medium sized systems
Software maintance
- Modifying a pogram after it has been put into use
- Maintance does not normally invole major changes
- Changes are implmented by modifying existing compontnents and adding new components to the system.
Maintance is inevitable
- the sys requirements are likely to change while being developed because the enviornment is changing.
- Systems are tightyly coupled with their enviornment, when a system is installed in a new environemnt it changes that enviornment therefore it changes sys. req.
- Systems MUST be maintained therefore to remain useful to an enviornment
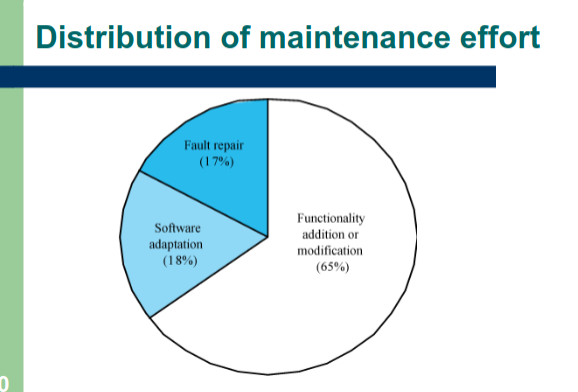
Types of maintenace (IMPORTANT)
- Software Faults
- Changing a system to correct deficiencies in the way meets its requirements
- Adapt software to a different operating environment
- Changing a system so that it operates in a different enviornment(computer, OS, etc.) from its initial implementation
- Add to or modify the systems Functionality
- modifying the system to satisfy new requirements
Possible questions:
- What are the 3 types of maintenaces
- Out of the 3 which are the most done
Maintenance cost factors (IMPORANT)
- Team Stability
- Maintenance costs are reduced if the same staff are involved with them for some time.
- Contractual Responsibility
- The developers of a system may have no contractual responsibility for maintenance so there is no incentive to design for future change.
- Staff skills
- Maintenance staff are often inexperienced and have limited domain knowledge.
- Program age and structure
- As programs age, their strucutre is degraded and they become harder to understand and change.
Complexity metrics
- Predictions of maintainability can be made by complexity metrics
- Complexity depnds on:
- Complexity of control strucutes
- complexity of data structures
- Object, method (procedure) and module size
Process Metrics
- Process measurements may be used to assess maintainability
- Number of requerest for corrective maintenance
- Average time required for impact analysis
- Average time taken to implement a change request
- Number of outstanding change requests
- If any or all of these are increasing, this may indicate a decline in maintainability
Evolution processes
- Depends on...
- The type of software being maintained
- The development processes used
- The skills and experience of people involved
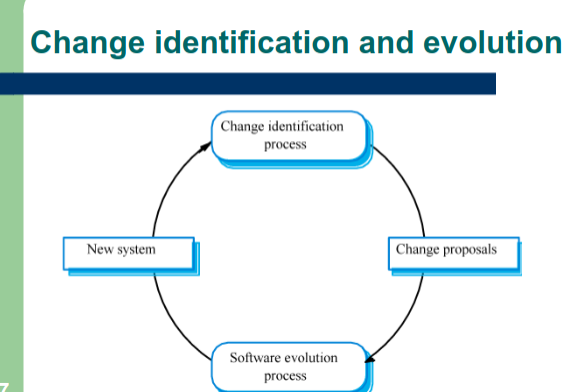
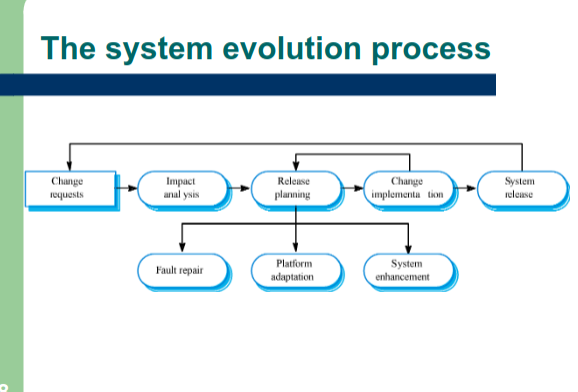
Know how to draw this
Urgent Change requests
- Urgent changes may have to be implements without going through all stages of SWE process
- if a serious system fault has to be repaired
- if changes to sys. env. (e.g. an OS upgrade) have unexpected effects
- if there are business changes that require a very rapid response.