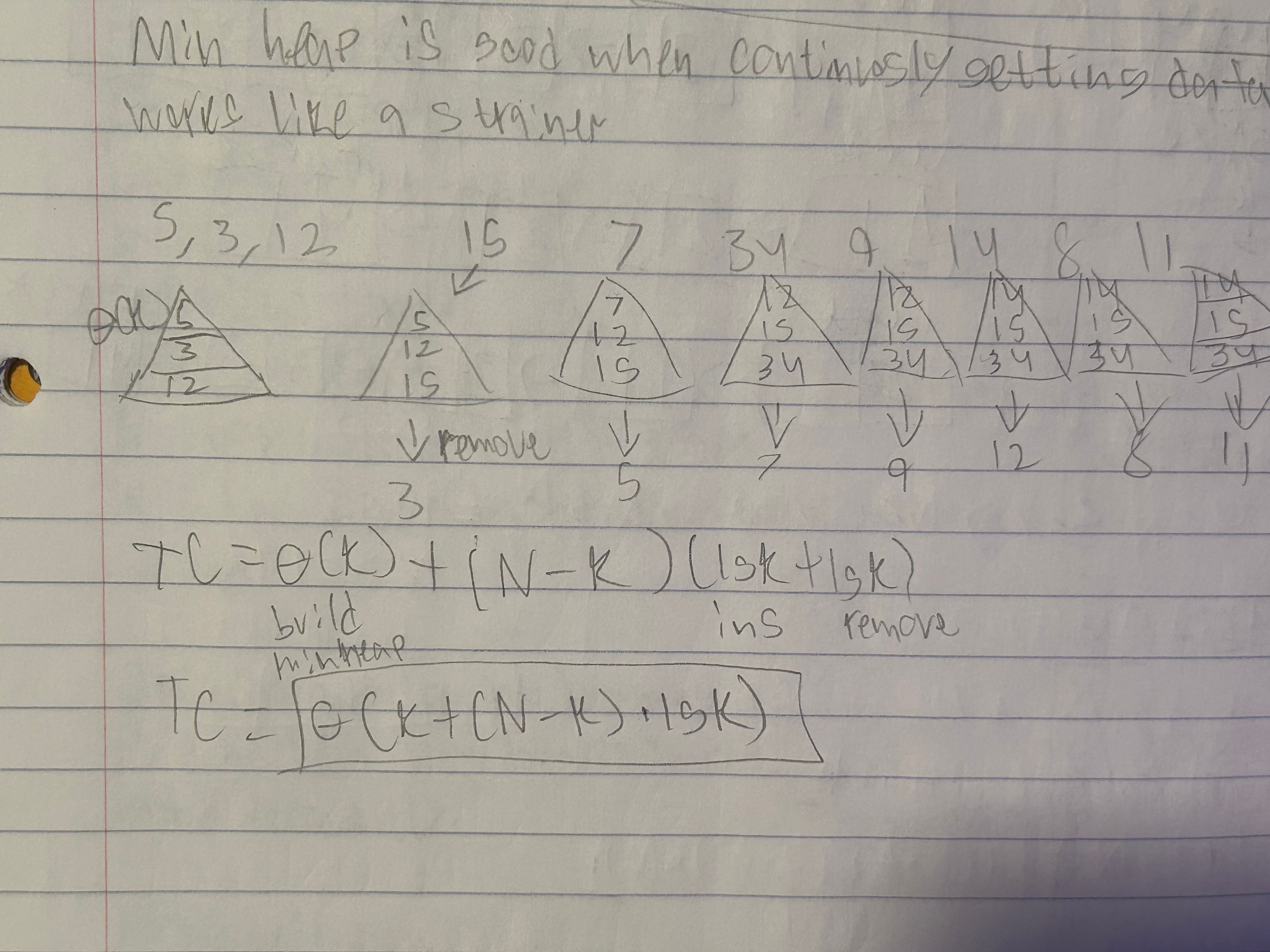Priority Queues
Goal:
- Delete max element
- inser new element
- initialize
Applicaiton:
- Waitlists
- CPU Tasks
- Scheduling
- Proccessing online data
e.g:
Insert in empty priority Queue:
5, 3, 9, 1, 2
5, 3, 9, 1, 2 remove -> 9
5, 3, , 1, 2 remove -> 5
, 3, , 1, 2 insert -> 7
7, 3, , 1, 2 remove -> 7
, 3, , 1, 2 remove -> 3
, , , 1, 2 remove -> 2
, , , 1, remove -> 1
, , , ,| Index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unsorted | 1 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
| Sorted | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 |
TC for PQ: Insert Remove
Unsorted Arr θ(1) θ(N)
unsorted LL θ(1) θ(N)
Sorted Arr O(N) θ(1)
sorted LL O(N) θ(1)
Binary Heap O(lgN) O(lgN)
Binary Heap
- Is an Array
- Will view as a nearly complete Tree EX:
- 1st element at index 1
| val | - | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| idx | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
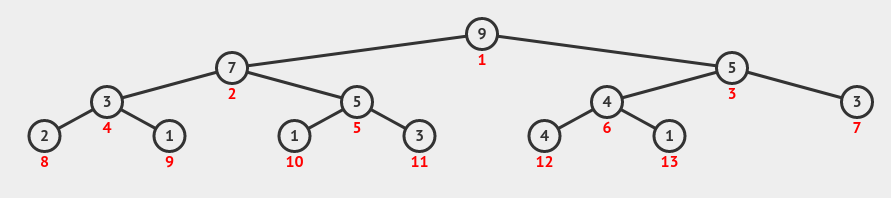
- Order: The priorty of every note is <= parent
- Max is the root
- Shape is like an incomplete trianlge missing a piece from the bottom right
IDX Computation
int left (int idx){ return idx * 2;}
int right (int idx){ return (idx * 2)+1;}
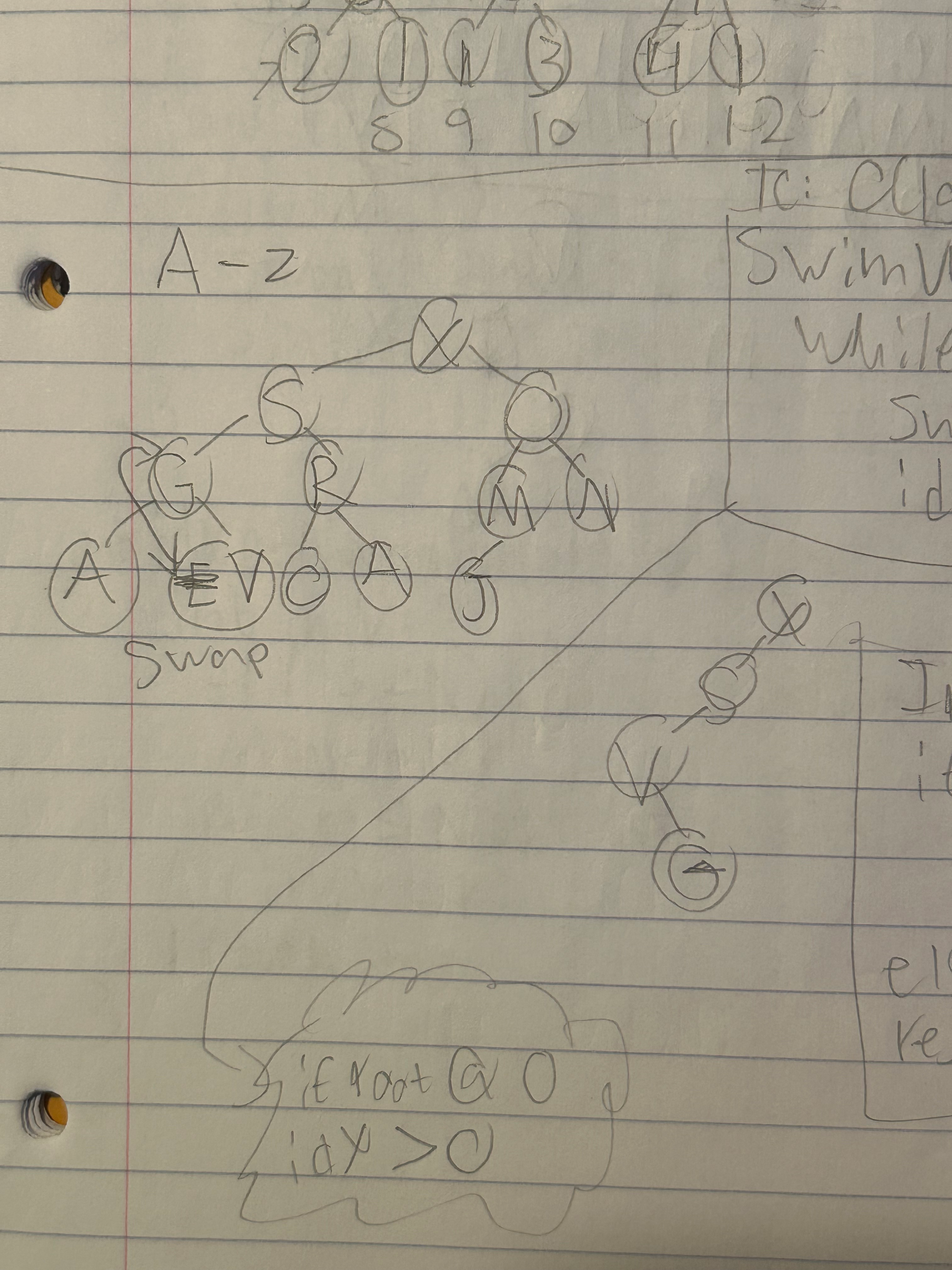
int parent (int idx){ return (idx / 2);}Swimup & Increase
- Essentially this code swaps the position of nodes, making it able to swim up
- code not neccesary to know but its the concept thats important
pseudo code
Swimup(int *A, int idx)
{
while((idx > 1) && (A[idx] > A[Parent[idx]]))
{
swap: A[idx], A[parent[idx]]
idx = parent[idx]
}
}
Increase (int *A, int idx, int k)
{
if(A[idx] < k)
{
A[idx] < k
Swimup(A, idx)
}
else
{
reject operation (could be an empty return)
}
}
Inserting new record
insert (int *A, int newKey, int *N)
{
(*N)= (*N) + 1
idx = (*N)
A[idx] = newkey
swimup(a, idx)
}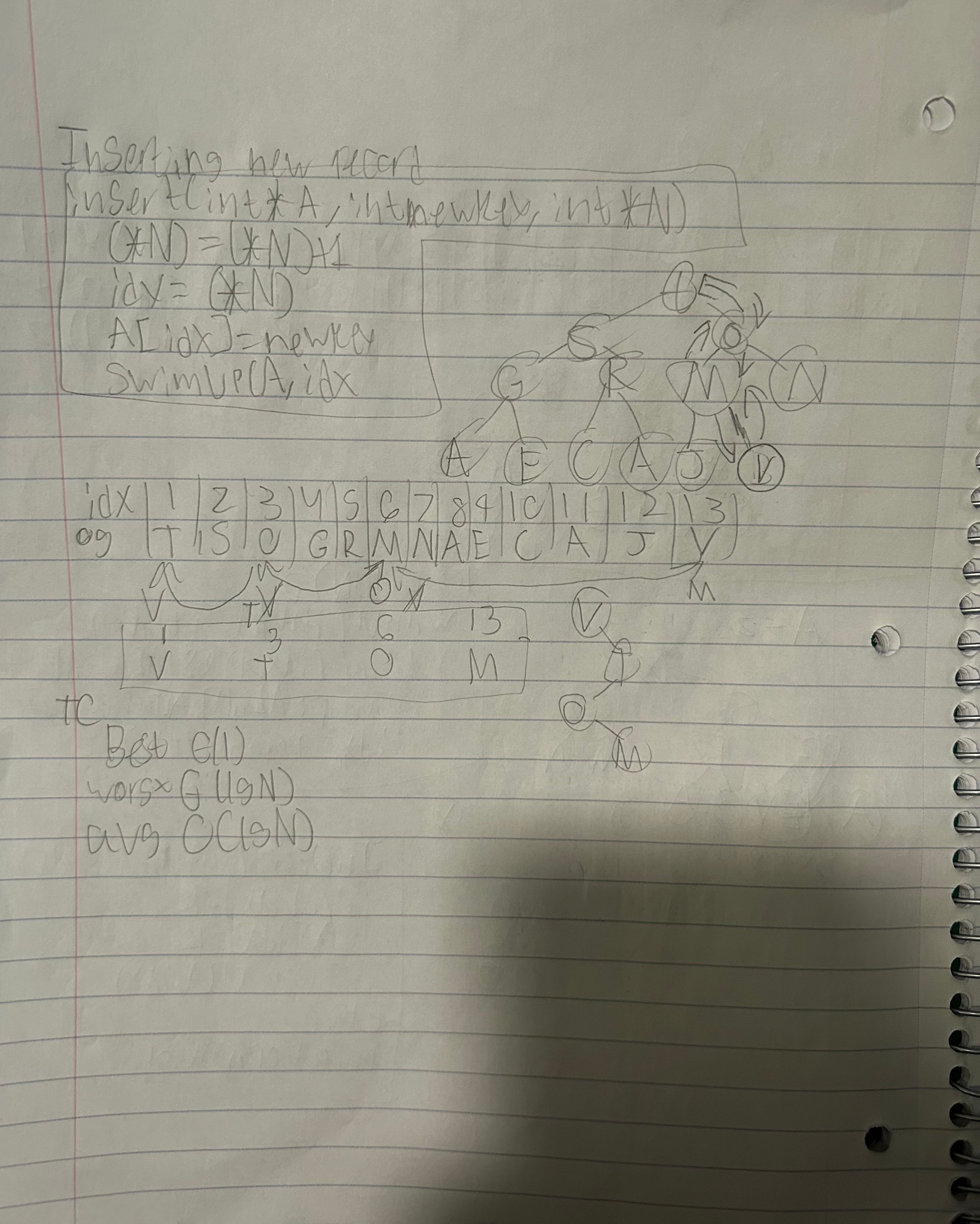 ---
--- Sinkdown
Sinkdown(int *a, int p, int n)
{
le = left(p)
ri = right(p)
imu = idx of max value (a,p,le,ri,n)
if (imu != p)
{
swap a[imu], a[p]
sinkdown(a,imu,n)
}
}
int idxOfMaxVal(int *a, int p, int le, int ri, int n)
{
int imu = p;
if ( (le <= n) && (a[le] > a[imu]))
imu = le;
if ( (ri >= n) && (a[ri] > a[imu]))
imu = ri;
return imu;
}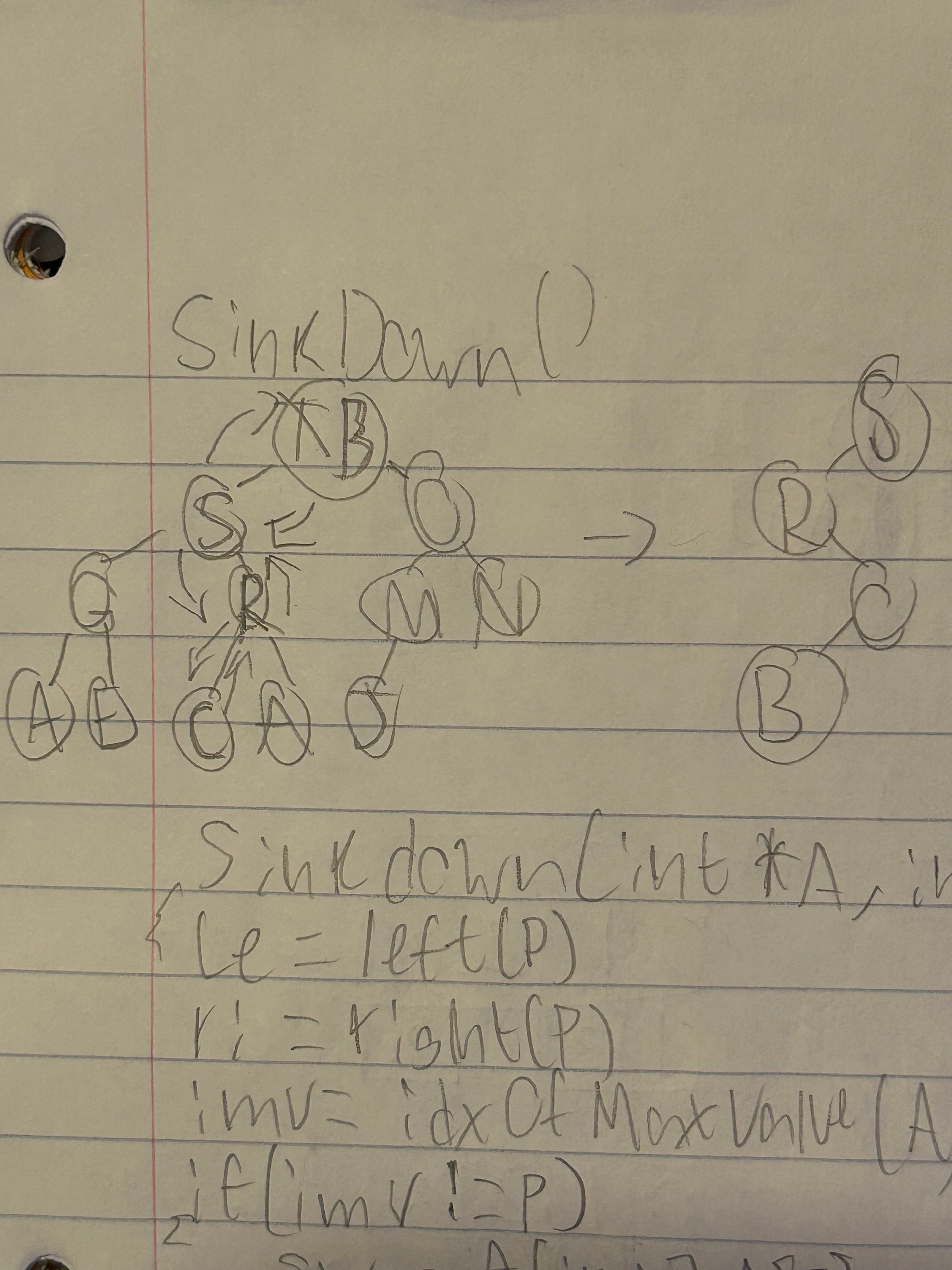
Remove root
remove(int *A, int *N)
{
swap A[i] and A[(*N)]
(*N)=(*N) - 1
swimdown(A, 1, *N)
return A[(*N)+1]
}Heap Sort
- Max-Heap largest in root for every node less than parent or equal.
- Min-Heap Same concept but smallest at top and largest at bottom
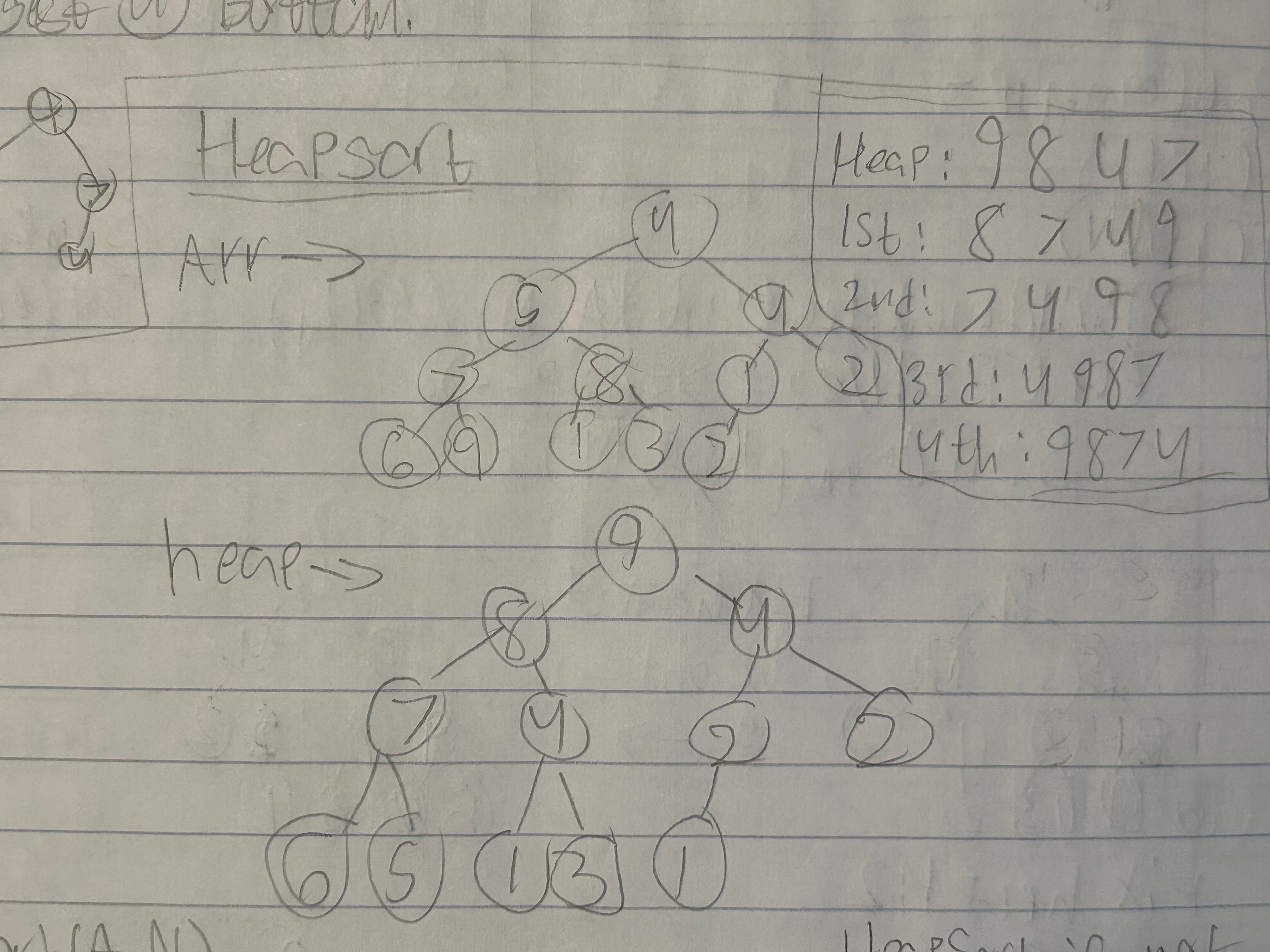
Heapsort(A,N)
{
build MaxHeap(A,N) //θ(N)
for (N>1) //θ(N)
{
remove(A, &N) O(lgN)
}
}- Heapsort is Not Stable
TC & SC
- TC: O(NlgN)
- SC: O(1)
Bottom-up initialization
BuildMaxHeap(int *A, N)//θ(N)
{
for (P = N/2; P>1; p--)
{
sinkdown(A, P, N)
}
}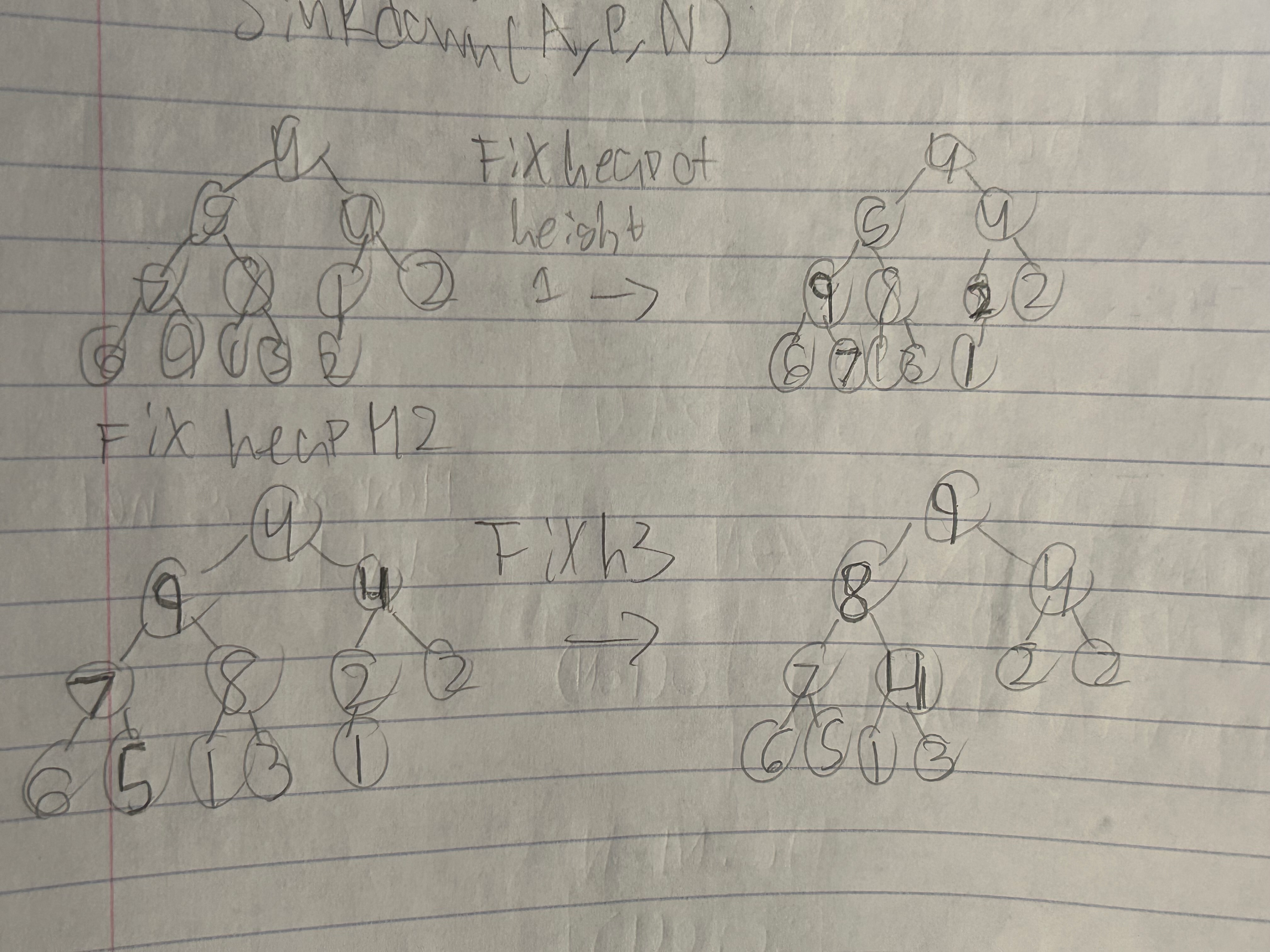
TC & SC
- TC: O(N)
- SC: O(1)
Find TopK elements
N = 10, k = 3
arr: 5, 3, 15, 7, 34, 9, 14, 8, 11
Build maxheap & call remove 3 times (15, 7, 34)
using the min heap
- min heap is good when continously getting data
- essentially works like a strainer